프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
풀이1
이렇게 푸니까 일단 통과는 하지만 테스트케이스 10번에서 시간이 오래 걸렸다.
- 일단 k개를 제외하고 number.length() - k 개수만큼 숫자를 골라야 한다. => 반복문
- 그리고 두번째 반복문에서는 각 회차에서 가장 큰 수(max)를 골라줘야 한다. 그런데 이 가장 큰 수를 고를 때 주의해야할 점이 있다. 바로 어디까지 중에서 (몇번째 인덱스까지) 가장 큰 수를 고를 것인가? 이다.
- 1924, k=2라면 max를 고를 때 192 중에서 골라야한다. 왜냐면 두개의 수를 골라야 하기 때문에 (k=2이므로 2개 숫자 제거) 예를 들어, 1879라고 생각해보면 무작정 9를 고르면 그건 가장 큰 수가 되지 못하기 때문이다.
- 그래서 아래 그림과 같이 생각을 하면서 규칙을 찾아 k + i 인덱스까지 중에서 회차마다 가장 큰 수를 골라서 append해준다.

class Solution {
public String solution(String number, int k) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int index = 0;
// 우리는 number.length() - k 개수를 숫자를 뽑을것이다
for (int i = 0; i < number.length() - k; i++) {
int max = 0;
//큰수를 만들기 위해 뒤 숫자들 중 가장 큰수를 뽑아서 붙여줘야 한다
for (int j = i; j <= i+k ; j++) {
if (number.charAt(j) - '0' > max) {
max = number.charAt(i) - '0';
index = j + 1; // 다음 숫자부터 골라야하므로
}
}
sb.append(max);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}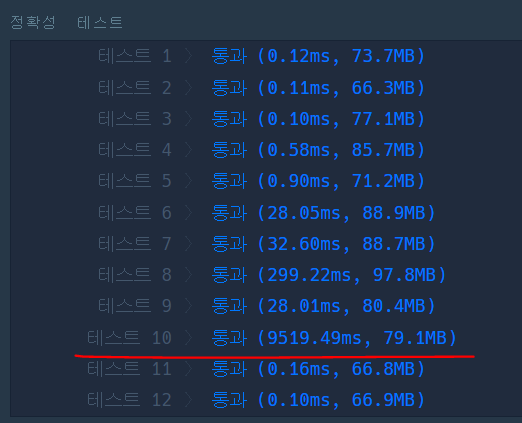
반복문을 두번돌아 테스트10에서 속도가 매우 느리다는 것을 알 수 있다.
풀이2
다른분들의 풀이를 보니 스택을 이용해서 푼 풀이도 있었다.
- 스택에 들어있는 문자(stack.peek()) 가 현재 i번째 문자(charAt(i))보다 작으면 꺼낸다.
- 문제는 k개의 숫자를 제거하는 것이므로, pop할때 k-- 로 k를 줄여준다.
- k개의 숫자가 pop되면(제거되면) 종료 후 스택에 있는 값을 꺼내준다.
이런식으로 풀면 왼쪽에서부터 (앞에서부터) k개의 작은 수를 차례로 제거할 수 있다.
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public String solution(String number, int k) {
char[] result = new char[number.length() - k];
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i=0; i<number.length(); i++) {
char c = number.charAt(i);
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() < c && k-- > 0) {
stack.pop();
}
stack.push(c);
}
for (int i=0; i<result.length; i++) {
result[i] = stack.get(i);
}
return new String(result);
}
}
'알고리즘 > 프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스/java] 위클리챌린지 2주차-상호평가 (0) | 2023.05.12 |
|---|